
- #Using ettercap and wireshark tutorial how to
- #Using ettercap and wireshark tutorial mac
- #Using ettercap and wireshark tutorial windows
We will use here the Ettercap plugin called dns_spoof to test a very famous attack, the DNSspoofing where the pirate answers DNS requests at the place of the DNS server. If you have a Netscreen (Juniper) device, use the following command to display the ARP table: Launch a command line interface window as follow:Ĭ:\Documents and Settings\administrator> arp -a
#Using ettercap and wireshark tutorial windows
Let's see if we successfully poisoned the router and windows machine ARP table:. This means that the packets between the Windows machine and the router will transit through the Ettercap machine.
#Using ettercap and wireshark tutorial mac
If we look at the router and Windows machine ARP table, we see that the Ettercap Linux machine poisoned their ARP table and replaced the router or Windows machine MAC addresses by its own MAC address. The difference between the two steps comes from the fact that there is no request coming from Windows (192.168.1.2) to find the MAC address associated to the router (192.168.1.1) because the poisoner continuously sends ARP packets telling the Windows machine that 192.168.1.1 is associated to his own MAC address (11:22:33:44:99:99) instead of the router MAC address (11:22:33:44:11:11).
The router ARP broadcast request is answered by the Windows machine similarly than in the previous capture.
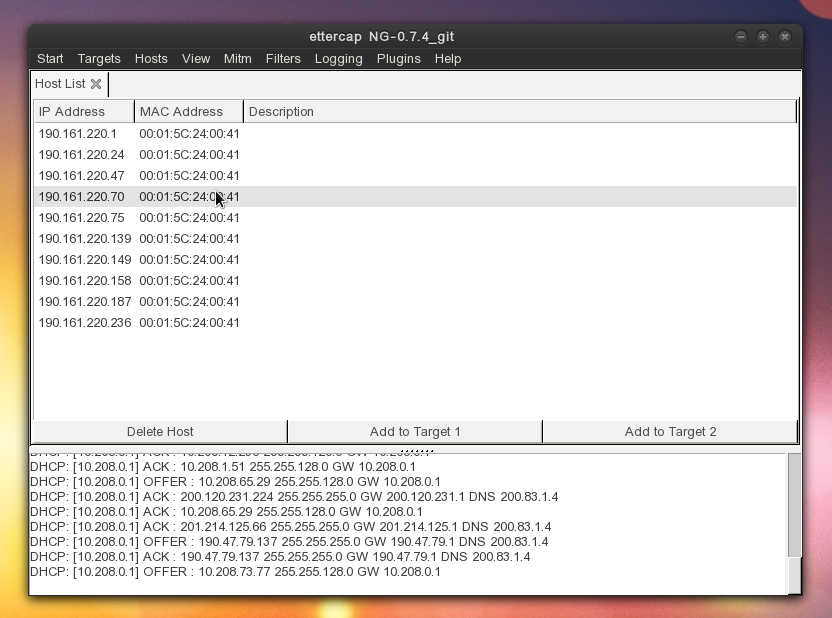
Finally, some countermeasures are given to fight against these damned ARP poisoning attacks.Īs a reminder: (See the network diagram) 192.168.1.1īefore being able to communicate together, the router and the Windows machine send an ARPbroadcast to find the MAC address of the other.
#Using ettercap and wireshark tutorial how to
In the ARP poisoning tutorial, we will explain how to configure the Ettercap machine as "man in the middle", then, in the filtering tutorial, we will show you some attacks. The goal of our tutorial is to provide warning about the danger of "man in the middle" attacks by ARP spoofing. Since Ettercap has to write (create) log files, it must be executed in a directory with the right permissions. After the initialization phase, the root privileges are not needed anymore, so Ettercap drops them to UID = 65535 (nobody). It can slow down the network performances between the two hosts because of the packets' machine process time.Įttercap needs root privileges to open the Link Layer sockets. Please note the following things about the Ettercap machine behaviour:Įvery time Ettercap starts, it disables IP forwarding in the kernel and begins to forward packets itself. After the ARP poisoning attack, The Ettercap machine with IP 192.168.1.100 is set as "man in the middle". In our tutorial, we will use the case study below where a machine with IP 192.168.1.2 reaches internet resources from a local network.

This attack is referred as ARP poisoning or ARP spoofing and is possible only if the pirate and the victims are inside the same broadcast domain which is defined on the host by an IP address and a Subnet mask, for example: 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 The pirate will answer to the caller with fake packets saying that the IP address is associated to its own MAC address and in this way, will "short-cut" the real IP - MAC association answer coming from another host. The attack comes when a machine asks the other ones to find the MAC address associated with an IP address. The caller will keep the IP - MAC association in its cache, the ARP cache, to speed up new connections to the same IP address. When a device tries to access a network resource, it will first send requests to other devices asking for the MAC address associated with the IP it wants to reach. The ARP protocol is a layer 3 protocol used to translate IP addresses (ex:192.168.1.1) to physical network card addresses or MAC addresses (ex:0fe1.2ab6.2398). There are several kinds of attacks to become "man in the middle", we will see in this tutorial attacks based on the ARP protocol. Once in this position, the pirate can launch a lot of different very dangerous attacks because he/she is in the way between to two normal machines.
This is an attack where a pirate put its machine in the logical way between two machines speaking together as shown in the picture below. Plugins are also available for attacks such as DNS spoofing. provide fake SSL certificates in HTTPS sections to the victims. discover passwords for protocols such as FTP, HTTP, POP, SSH1, etc. infect, replace, delete data in a connection For those who do not like the Command ike Interface (CLI), it is provided with an easy graphical interface.Įttercap is able to perform attacks against the ARP protocol by positioning itself as "man in the middle" and, once positioned as this, it is able to: On the Windows machine, with the help of Wireshark, we can compare the ARP traffic before and after the poisoning:Įttercap is a tool made by Alberto Ornaghi (ALoR) and Marco Valleri (NaGA) and is basically a suite for man in the middle attacks on a LAN.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
